Combination of Metabolic and Restrictive
Mixed techniques combine gastric restriction with neuro-hormonal effects through the creation of a bypass, diversion or excision of metabolically active cells:
- Gastric bypass
- Sleeve gastrectomy or longitudinal gastrectomy
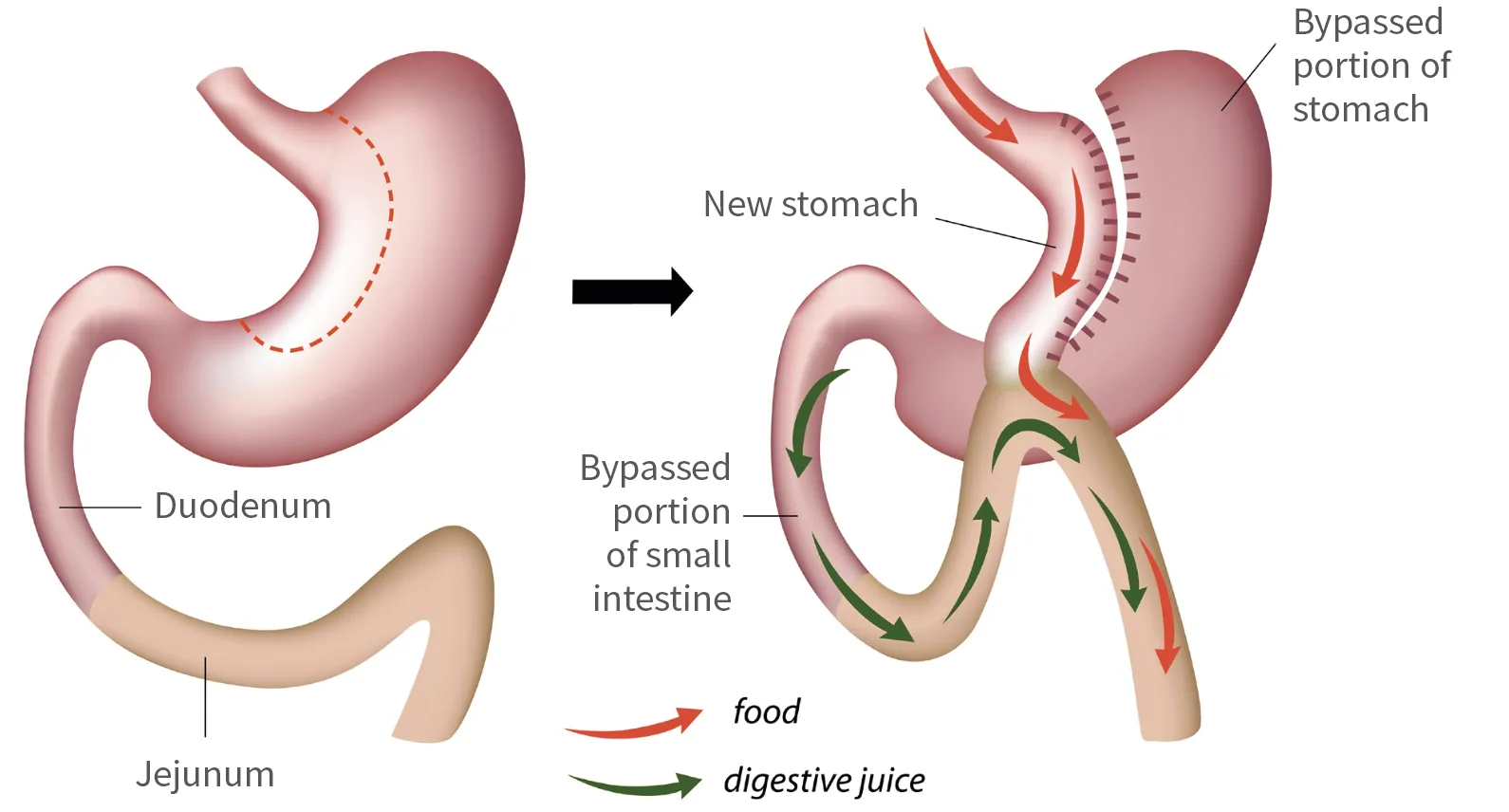
Gastric Bypass
- international ‘gold standard’
- involves construction of a very small ‘pouch’ from a part of the top of the stomach. This is then joined to the small bowel, bypassing the rest of the stomach and about one metre of the small intestine
- reduces amount that can be eaten at a single sitting, and reduces hunger, probably by affecting the hormones in the gut
- good balance between efficacy and the durability of the weight loss.
Advantages
- effective, long-lasting weight loss for most people, and most obesity-related health problems improve
- improved quality of life
- normal (especially healthy) food can still be eaten, just in small volumes.
Disadvantages
- vitamin supplements should be taken daily, and usually iron and calcium tablets
- the risk of gastric bypass surgery is similar to elective hip or knee surgery (1 in 200 to 1 in 1000 risk to life)
- early complications can occur soon after the surgery due to leaks from where the gut is joined; bleeding; infection; or blood clots
- late complications can occur due to blockages of the bowel, not easily reversed
- not everyone is a candidate for laparoscopic bypass; these people may require open surgery or should consider other options
- even this operation can be beaten by eating the wrong foods and failing to keep to the necessary lifestyle changes.
Expected weight loss
About 75 per cent of excess weight
Duration of operation
2 to 3 hours
Number of nights in hospital
2 to 3
Recovery period
1 to 2 weeks off work, occasionally up to 4 weeks
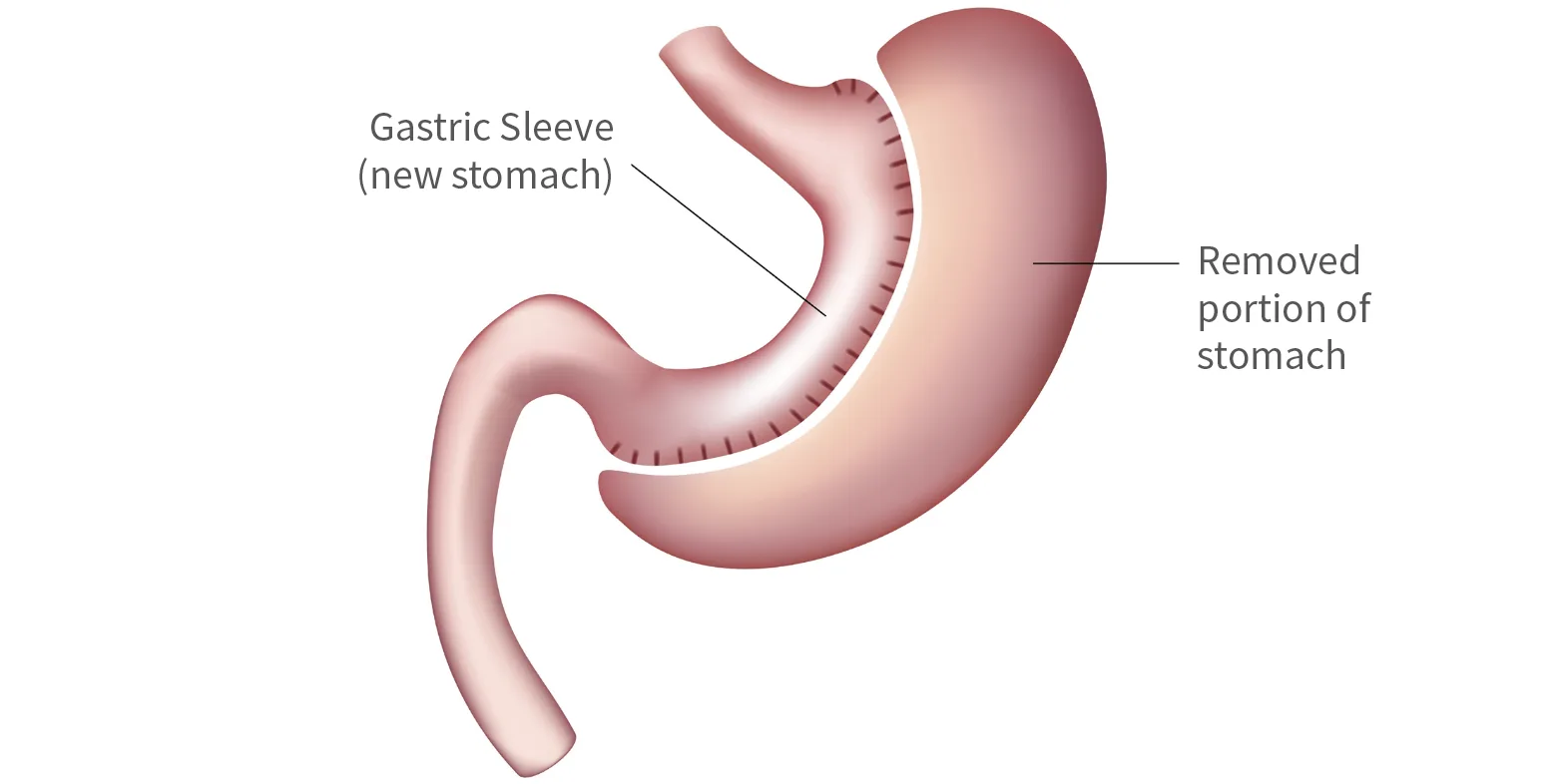
Sleeve Gastrectomy
- reduces the size of the stomach from a sac to a narrow tube.
- weight is lost because the patient feels fuller earlier after eating, largely due to the smaller size of the stomach. The procedure also reduces some appetite simulating hormones produced by the stomach. Apart from this effect, the stomach digests calories and nutrients in an almost normal way.
Advantages
- effective weight loss for most people and improvement in many obesity-related health problems improve
- normal (especially healthy) food can still be eaten, just in small volumes
- good option for high-risk patients.
Disadvantages
- vitamin supplements should be taken daily
- long-term outcomes uncertain
- early complications can occur soon after the surgery and be due to leaks from where the gut is stapled, bleeding, infection or blood clots
- irreversible
- even this operation can be beaten by eating the wrong foods and failing to keep to the necessary lifestyle change.
Expected weight loss
About 50 to 75 per cent of excess weight
Duration of operation
2 hours
Number of nights in hospital
1 to 2
Recovery period
1 to 2 weeks off work.
No longer supported
- Adjustable Gastric Banding
This procedure involves placing an adjustable band around the upper part of the stomach to reduce hunger and promote early fullness. While still used overseas, it does not provide the sustainable results achieved with gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy. For this reason, Auckland Weight Loss Surgery no longer supports or recommends gastric banding.

