One anastomosis (mini) gastric bypass surgery
This procedure is a highly effective procedure that combines the benefits of both gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. It’s a simpler, single-anastomosis version of the Roux-en-Y bypass and has shown excellent results for weight loss and improvement in obesity-related conditions.
The one anastomosis (mini) gastric bypass involves two key changes to your digestive system:
- Creating a smaller, narrow pouch from the stomach (similar to the shape of a sleeve gastrectomy).
- Bypassing a section of the small intestine, so food travels directly from the pouch into the intestine further down.
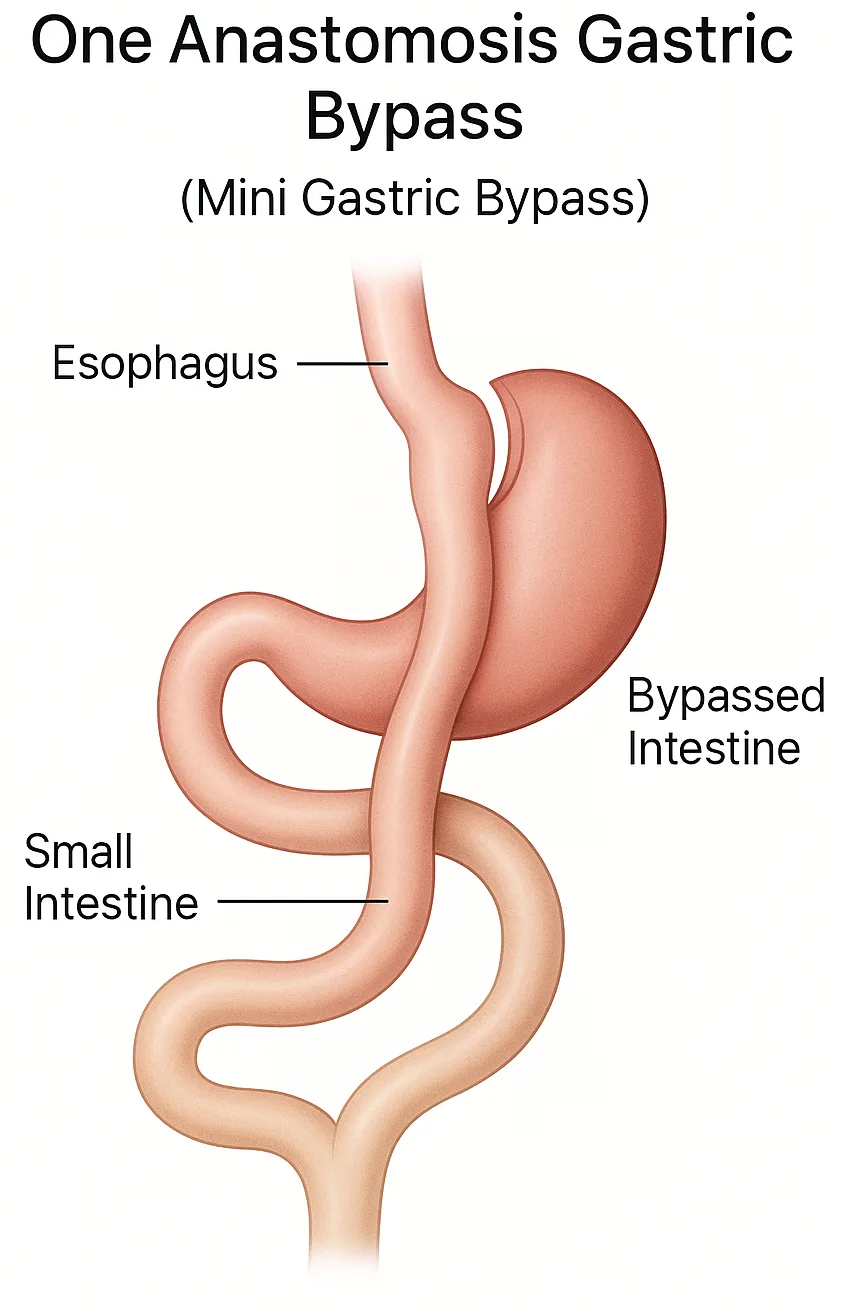
This simplified diagram shows how food bypasses part of the stomach and intestine in OAGB, limiting both food intake and absorption.
Pros of OAGB surgery
- Significant and sustained weight loss
- High resolution of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic conditions
- Shorter operating time than traditional gastric bypass
- Simpler surgical technique (one join instead of two)
- Lower risk of internal hernias compared to Roux-en-Y
- Stomach remains accessible for future endoscopy
Cons of OAGB surgery
- Risk of bile reflux due to the direct connection between the stomach pouch and small bowel
- Higher risk of nutritional deficiencies, especially in iron, calcium, and B vitamins
- Dumping syndrome can occur if high-sugar foods are eaten
- Long-term vitamin and mineral supplementation required

